How much do SMAP brightness temperature observations and gauge-based precipitation data contribute to the skill of the SMAP Level-4 Soil Moisture product?
Soil moisture provides an important connection between the land surface water, energy, and carbon cycles. By merging Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite brightness temperature (Tb) observations and gauge-based precipitation data into a numerical model of land surface water and energy balance processes, NASA generates the global, 9-km resolution, 3-hourly Level-4 Soil Moisture (L4SM) data product, which is published with ~2.5-day latency to support Earth science research and applications such as drought monitoring.
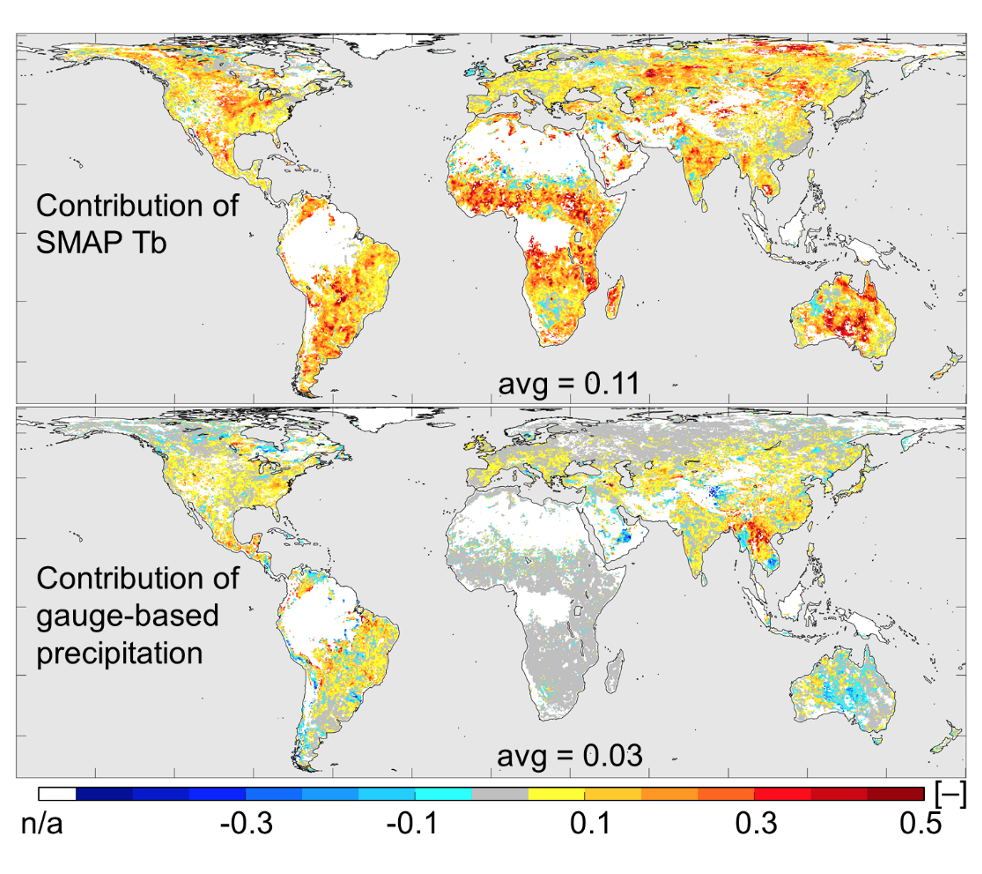
Using additional model simulations and validation against independent measurements, we find that the SMAP Tb observations contribute more to L4SM surface soil moisture skill than do the gauge-based precipitation data (Figure 1). SMAP’s contribution to L4SM skill is particularly large in poorly instrumented regions, including portions of South America, Africa, and central Australia. Both data sources contribute about equally to L4SM root-zone soil moisture skill and L4SM runoff skill largely stems from gauge-based precipitation data (not shown).
Reference:
Reichle, R. H. et al. (2020), The Contributions of Gauge-Based Precipitation and SMAP Brightness Temperature Observations to the Skill of the SMAP Level-4 Soil Moisture Product, J. Hydromet., in press, doi:10.1175/JHM-D-20-0217.1.


